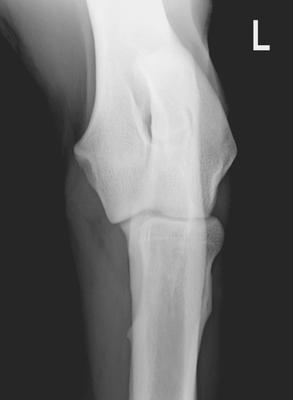
Elbow Dysplasia
Technique for ED Radiographs
To diagnose elbow joint dysplasia, two radiographic projections of the elbow are performed. Correct positioning of the dog is essential for obtaining a clear and accurate image of the joint.
Projections
ED medio-lateral radiograph
- The dog must be deeply sedated or anesthetized.
- No handler is required to hold the dog.
- The elbow is flexed at an angle of 60° to approximately 90° and the central beam is centered on the elbow joint.
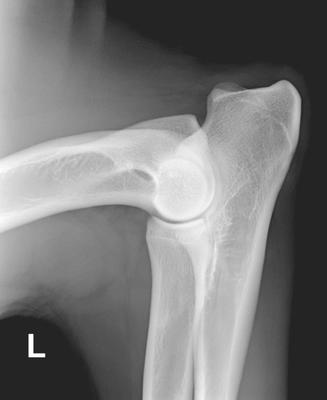
ED craniocaudal radiograph in 15° pronation (craniocaudal-15°-lateral-caudomedial)
- The dog must be deeply sedated or anesthetized.
- No handler is required to hold the dog.
- The elbow is fully extended for this view.
- The joint is represented in pronation at 15°.